By CBD Mind Lab Editorial Team | Reviewed by Medical Professionals
What Are Psychedelic Drugs? Psychedelic drugs, also known as hallucinogens, are powerful substances that alter perception, mood, and cognitive processes. While they have been used for centuries in spiritual and medicinal contexts, modern research is once again exploring their potential therapeutic benefits for conditions like depression, anxiety, PTSD, and chronic pain.
In this article, we explore what psychedelic drugs are, their types, effects, risks, and the emerging field of psychedelic therapy.
What Are Psychedelic Drugs?
Psychedelics are substances that profoundly affect how you perceive the world around you. They can cause hallucinations, alter your sense of time and space, and intensify emotional experiences. Historically, many indigenous cultures have used these substances in spiritual rituals for centuries. Today, scientific interest in psychedelics is growing rapidly due to their potential for treating various mental health conditions.
⚠ Important: While some research shows promise, many psychedelics remain illegal or strictly controlled outside of clinical trials. Always consult with a healthcare professional before considering any psychedelic treatment.
Related article: CBD vs. Psychedelics: How They Compare for Mental Health
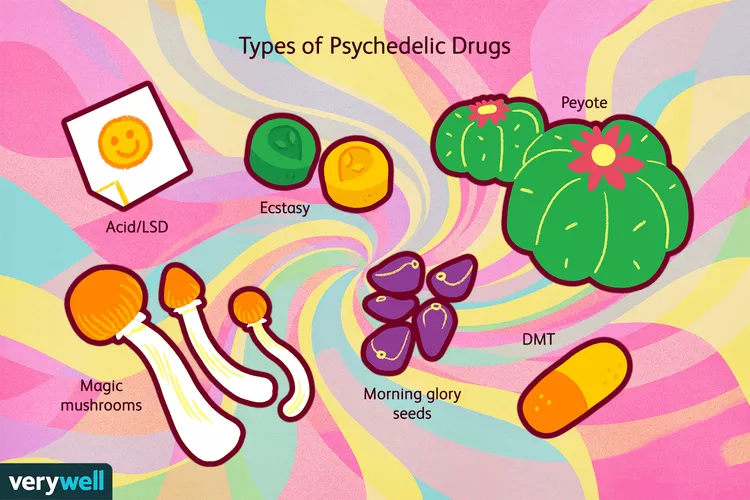
Types of Psychedelic Drugs
Psychedelics come in many forms — some natural, others synthetic. Here are the most common types:
1️⃣ LSD (Lysergic Acid Diethylamide)
- Synthetic hallucinogen derived from ergot fungus.
- Known as “acid”, popularized in the 1960s.
- Causes intense hallucinations, time distortion, and heightened sensory experiences.
Learn more: LSD Facts – National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA)
2️⃣ Psilocybin (Magic Mushrooms)
- Naturally occurring psychedelic in certain fungi.
- Known for inducing visual and auditory hallucinations.
- Early research suggests potential for treating depression and anxiety.
3️⃣ DMT (Dimethyltryptamine)
- Found naturally in various plants.
- Short but intense psychedelic experience (often called “the spirit molecule”).
- Commonly used in traditional South American ayahuasca ceremonies.
4️⃣ Mescaline (Peyote)
- Found in peyote cactus.
- Used for spiritual ceremonies by Native American tribes.
- Similar hallucinogenic effects to LSD.
5️⃣ Ololiuqui (Morning Glory Seeds)
- Naturally occurring psychedelic from morning glory seeds.
- Historically used in Central and South American rituals.
6️⃣ MDMA (Ecstasy)
- Known more for its stimulant and empathogenic effects.
- Shows promise in treating PTSD when used under medical supervision.
- Currently classified as a Schedule I substance but in active clinical trials.
Related resource: FDA’s Guidance on Psychedelic Research (2023)
Effects of Psychedelic Drugs
The effects vary widely based on dosage, individual physiology, and environment (often referred to as “set and setting”).
Common effects include:
- Altered perception of time and space
- Visual and auditory hallucinations
- Heightened sensory awareness
- Emotional intensity (positive or negative)
- Feelings of spiritual connection or insight
- Nausea or physical discomfort
Short-term physical effects may include:
- Elevated heart rate and blood pressure
- Sweating or chills
- Dizziness
- Dry mouth
- Muscle tremors
🧠 Interesting Fact: Some users report profound “ego dissolution” — a feeling of merging with the universe — particularly with high doses of LSD or psilocybin.
Tolerance and Addiction Potential
Unlike many other substances, most psychedelics are not physically addictive. However, tolerance can develop rapidly, especially with substances like LSD and psilocybin.
- Tolerance: Repeated use reduces effects, requiring higher doses for the same experience.
- Cross-tolerance: Tolerance to one psychedelic may reduce sensitivity to others (e.g., LSD tolerance may affect psilocybin response).
- Addiction: Classic psychedelics have low addiction potential. However, MDMA carries a higher risk of misuse.
If you or someone you know needs help with substance use, contact the SAMHSA National Helpline at 1-800-662-4357.
The Emerging Field of Psychedelic Therapy
In recent years, clinical studies have reignited interest in using psychedelics for therapeutic purposes, including:
- Depression
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Anxiety Disorders
- Substance Use Disorders
- Chronic Pain (in combination with CBD)
🔬 In June 2023, the FDA released guidelines to support safe, effective psychedelic research protocols. As of 2025, psychedelic-assisted therapy is still limited to controlled clinical trials.
Related blog: CBD and Psychedelic Therapy: A New Frontier
What Are Psychedelic Drugs and Are they Legal?
In the United States, most psychedelics remain Schedule I controlled substances, meaning:
- Illegal for recreational use
- Allowed only in limited clinical or religious settings (e.g., Native American Church for peyote)
Important Note: Some U.S. cities and states (such as Oregon and Colorado) are beginning to decriminalize or legalize certain psychedelics under regulated frameworks.
Learn more: Psychedelic Legalization Map 2025 (MAPS)
Should You Try Psychedelics?
If you’re considering psychedelic therapy, remember:
✅ Only use under professional supervision.
✅ Be aware of legal restrictions in your area.
✅ Discuss your medical history with a qualified healthcare provider.
✅ Consider alternative options like CBD for Anxiety & Pain Relief.
Conclusion
What Are Psychedelic Drugs? Psychedelic drugs offer a fascinating and rapidly developing area of medical research, particularly for mental health disorders. While early results are promising, psychedelics are not a cure-all and carry significant risks if used irresponsibly. As scientific understanding continues to grow, psychedelic therapies may become more accessible — but for now, caution and expert guidance are essential.